Excel TEXT Function: Convert Numbers to Text Format
Introduction
In Excel, numbers and dates are typically stored as internal numeric values, which is convenient for calculations but not always suitable for direct display. The TEXT function is a powerful tool that can convert numbers, dates, and times into text with specific formats, making data more intuitive and readable. This article will detail the various uses of the TEXT function, including date formatting, number formatting, and custom text formatting, helping you enhance the presentation of your Excel data.
1. TEXT Function Basics
What is the TEXT Function?
The TEXT function is used to convert a value to text with a specific format and is an important function for data formatting in Excel.
Syntax
=TEXT(value, format_text)- value: Required parameter, representing the number, date, or time to convert
- format_text: Required parameter, representing the format code to apply, enclosed in quotes
How to Use Basic TEXT
- Select the cell where you want to display the result
- Enter
=TEXT( - Select the value cell to convert, or enter a specific value
- Enter a comma and the format code (enclosed in quotes)
- Press Enter to complete
Example
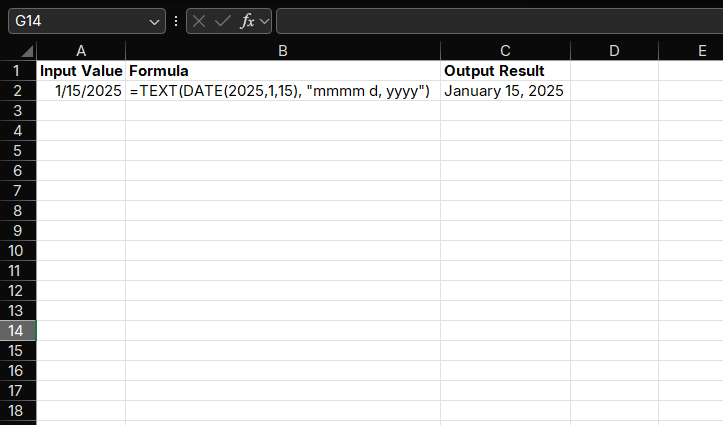
Suppose we have a date value 2025-01-15 and want to format it as "January 15, 2025", we can use:
=TEXT(DATE(2025,1,15), "mmmm d, yyyy")The result will display as "January 15, 2025".
Use Cases
- Convert dates to text with specific formats
- Format currency display
- Customize number display formats
- Create personalized string combinations
2. Date Formatting
Basic Date Formats
The TEXT function supports multiple date format codes, here are some commonly used formats:
| Format Code | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| yyyy | Four-digit year | 2025 |
| yy | Two-digit year | 25 |
| m | Month (1-12) | 1 |
| mm | Month (01-12) | 01 |
| mmm | Abbreviated month name | Jan |
| mmmm | Full month name | January |
| d | Day (1-31) | 15 |
| dd | Day (01-31) | 15 |
| ddd | Abbreviated weekday | Wed |
| dddd | Full weekday | Wednesday |
Example
Convert date values to different formats:
=TEXT(A1, "yyyy/mm/dd") // 2025/01/15
=TEXT(A2, "mm/dd/yyyy") // 01/15/2025
=TEXT(A3, "mmm d, yyyy") // Jan 15, 2025
=TEXT(A4, "dddd, mmmm d, yyyy") // Wednesday, January 15, 2025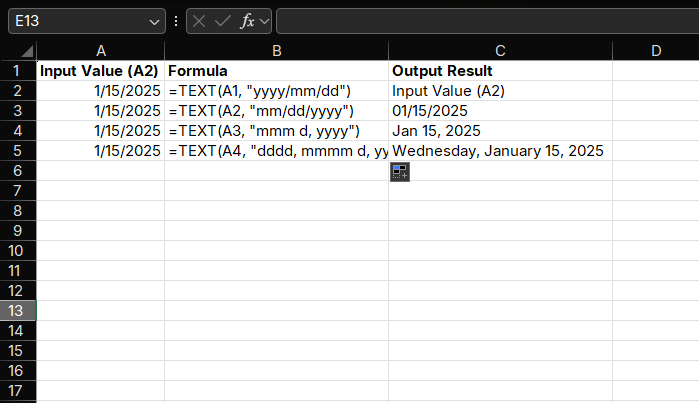
Practical Date Formatting
Example 1: Fiscal Year Display
Convert dates to fiscal year format (assuming fiscal year starts in July):
=TEXT(A2, "yyyy") & "-" & TEXT(DATE(YEAR(A2), MONTH(A2)+1, 1), "yy")For August 1, 2025, the result will display as "2025-26".
Example 2: Relative Date Display
Display relative dates such as "Today", "Yesterday", "Tomorrow":
=IF(A2=TODAY(), "Today", IF(A2=TODAY()-1, "Yesterday", IF(A2=TODAY()+1, "Tomorrow", TEXT(A2, "mmmm d, yyyy"))))3. Number Formatting
Basic Number Formats
The TEXT function supports multiple number format codes, here are some commonly used formats:
| Format Code | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Digit placeholder, displays digits, shows 0 for missing digits | 123.45 → 123.5 (using 0.0 format) |
| # | Digit placeholder, displays digits, shows nothing for missing digits | 123.45 → 123.5 (using #.# format) |
| . | Decimal point placeholder | 123.45 → 123.45 |
| , | Thousands separator | 123456 → 123,456 |
| % | Percentage format | 0.75 → 75% |
| $ | Currency symbol | 123.45 → $123.45 |
Example
Convert numeric values to different formats:
=TEXT(A1, "0.00") // 123.456 → 123.46
=TEXT(A2, "#,###.00") // 1234.56 → 1,234.56
=TEXT(A3, "0%") // 0.75 → 75%
=TEXT(A4, "$#,###.00") // 1234.56 → $1,234.56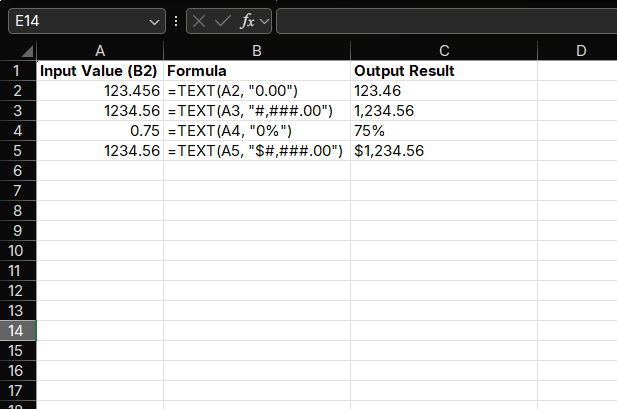
Currency Formatting
Example: Multi-Currency Display
Display different currency symbols based on currency code:
=IF(C2="USD", TEXT(B2, "$#,###.00"), IF(C2="EUR", TEXT(B2, "€#,###.00"), IF(C2="GBP", TEXT(B2, "£#,###.00"), TEXT(B2, "#,###.00"))))Percentage Formatting
Example: Growth Rate Display
Format growth rate as a percentage with sign:
=TEXT(B2, "+0.0%" & IF(B2<0, "", "+")) // 0.05 → +5.0%, -0.03 → -3.0%4. Time Formatting
Basic Time Formats
The TEXT function supports multiple time format codes, here are some commonly used formats:
| Format Code | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| h | Hour (0-23 or 1-12) | 14 → 2 (using h:mm AM/PM format) |
| hh | Hour (00-23 or 01-12) | 2 → 02 (using hh:mm format) |
| m | Minute (0-59) | 5 → 5 |
| mm | Minute (00-59) | 5 → 05 |
| s | Second (0-59) | 3 → 3 |
| ss | Second (00-59) | 3 → 03 |
| AM/PM | 12-hour clock indicator | 14:30 → 2:30 PM |
Example
Convert time values to different formats:
=TEXT(A2, "hh:mm") // 14:30:45 → 14:30
=TEXT(A3, "h:mm AM/PM") // 14:30:45 → 2:30 PM
=TEXT(A4, "hh:mm:ss") // 14:30:45 → 14:30:45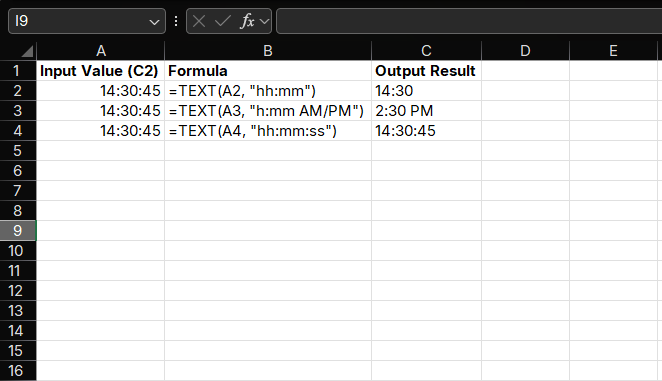
Duration Formatting
Example: Elapsed Time Display
Display elapsed time, such as "2 hours 30 minutes":
=TEXT(C2-B2, "[h] hours mm minutes") // Assuming B2=10:00, C2=12:30 → 2 hours 30 minutes5. Custom Text Formats
Combining Text and Formatted Values
The TEXT function can be combined with other text to create custom strings.
Example 1: Invoice Number Generation
Generate invoice numbers in the format "INV-2025-001":
="INV-" & TEXT(A2, "yyyy") & "-" & TEXT(B2, "000")Example 2: Personalized Greeting
Create a personalized greeting:
="Dear " & A2 & ", your order placed on " & TEXT(B2, "mmmm d, yyyy") & " has been shipped."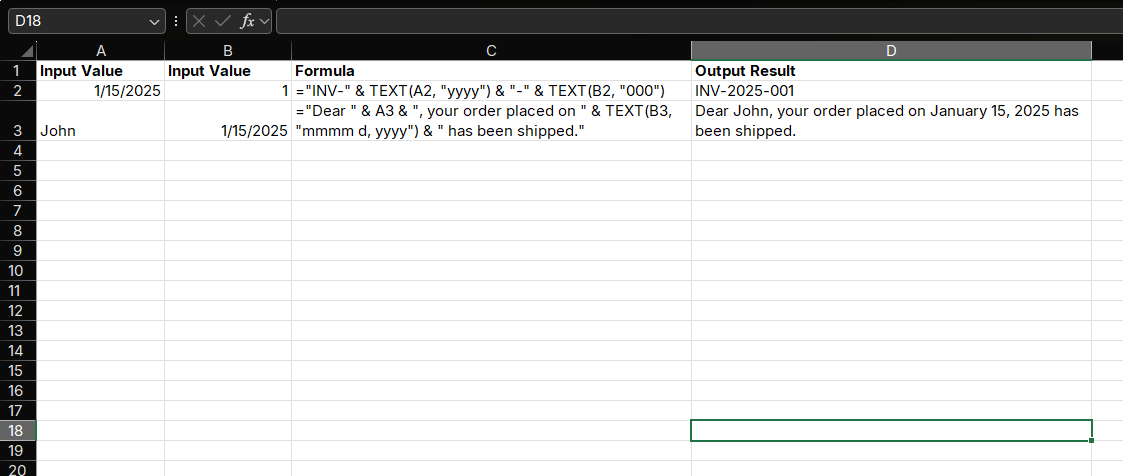
Conditional Text Formatting
Combine with IF function to create conditional text formats:
Example: Performance Rating
Display ratings based on sales performance:
=IF(B2>=10000, "Excellent (" & TEXT(B2, "#,###") & ")", IF(B2>=5000, "Good (" & TEXT(B2, "#,###") & ")", "Average (" & TEXT(B2, "#,###") & ")"))6. Advanced TEXT Function Applications
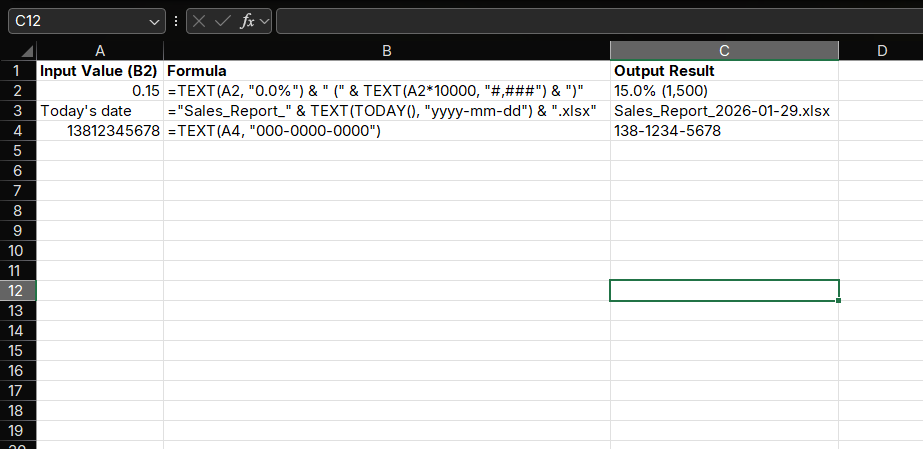
Example 1: Dynamic Chart Labels
Create dynamic chart labels combining values and percentages:
=TEXT(B2, "0.0%") & " (" & TEXT(B2, "#,###") & ")"Example 2: File Name Generation
Generate file names with dates:
="Sales_Report_" & TEXT(TODAY(), "yyyy-mm-dd") & ".xlsx"The result will display as "Sales_Report_2025-01-15.xlsx".
Example 3: Phone Number Formatting
Format 11-digit phone numbers to "XXX-XXXX-XXXX" format:
=TEXT(B2, "000-0000-0000")For 13812345678, the result will display as "138-1234-5678".
7. Notes on Using the TEXT Function
1. TEXT Function Returns Text
Values converted using the TEXT function become text format and cannot be directly used for mathematical calculations. If calculations are needed, use the original numeric values.
2. Format Codes are Case-Sensitive
Some format codes are case-sensitive. For example, "AM/PM" and "am/pm" produce the same result, but "YYYY" and "yyyy" may behave differently.
3. Regional Settings Affect Date Formats
Date formats may be affected by system regional settings. For example, "mmm" displays Chinese month abbreviations in Chinese systems and English month abbreviations in English systems.
4. Alternative: Cell Formatting
The TEXT function is suitable when you need to use formatted results as text. If you just need to change the display format of a cell without changing the value type, you can directly use cell formatting (right-click menu → Format Cells).
Summary
The TEXT function is a powerful data formatting tool in Excel that can convert numbers, dates, and times into text with specific formats, making data more intuitive and readable. Through this article, you should have mastered:
- The basic syntax and usage of the TEXT function
- Techniques for formatting dates and times
- Methods for formatting numbers and currencies
- Creating custom text formats
- Advanced TEXT function application examples
By proficiently using the TEXT function, you will be able to enhance the presentation of your Excel data and create more professional and intuitive reports and charts.
Have a problem with Excel or Google Sheets?
Tell us about the issue you're facing, and we'll create a step-by-step guide for it.