Excel COUNT Function Tutorial: Master Data Counting
Introduction
The COUNT function family is essential for data analysis in Excel. These functions allow you to count cells based on specific criteria, providing valuable insights into your data.
This tutorial will guide you through all the COUNT functions, from basic counting to advanced conditional counting, with practical examples you can apply immediately.
Basic COUNT Function
The COUNT function counts the number of cells that contain numbers.
Syntax
=COUNT(value1, [value2], ...)Arguments Explained:
- value1: The first cell range or value to count (required)
- value2, ...: Additional cell ranges or values (optional, up to 255)
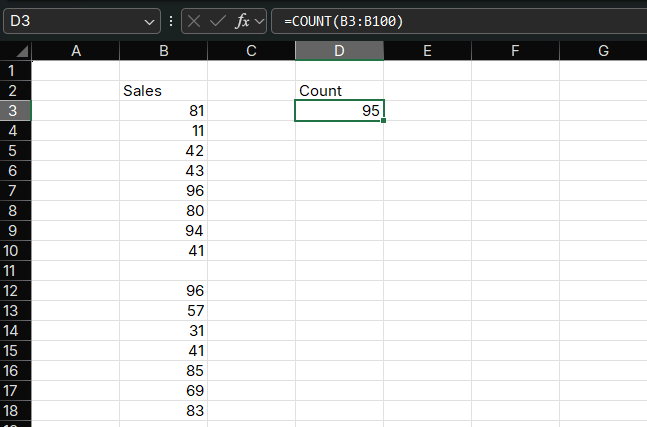
Example 1: Counting Sales Transactions
Suppose you have sales data in column A and want to count how many transactions were recorded.
Formula:
=COUNT(A2:A100)How it works:
- Counts only cells with numeric values in the range A2:A100
- Ignores text, blank cells, and errors
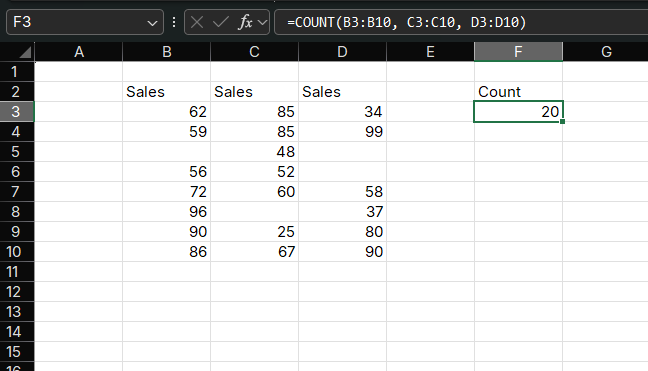
Example 2: Counting Multiple Ranges
You can count cells across multiple ranges:
Formula:
=COUNT(B2:B10, D2:D10, F2:F10)How it works:
- Counts numeric values in three separate columns
- Returns the total count across all ranges
COUNTA Function
COUNTA (Count All) counts the number of non-empty cells.
Syntax
=COUNTA(value1, [value2], ...)Arguments Explained:
- value1: The first cell range or value to count (required)
- value2, ...: Additional cell ranges or values (optional)
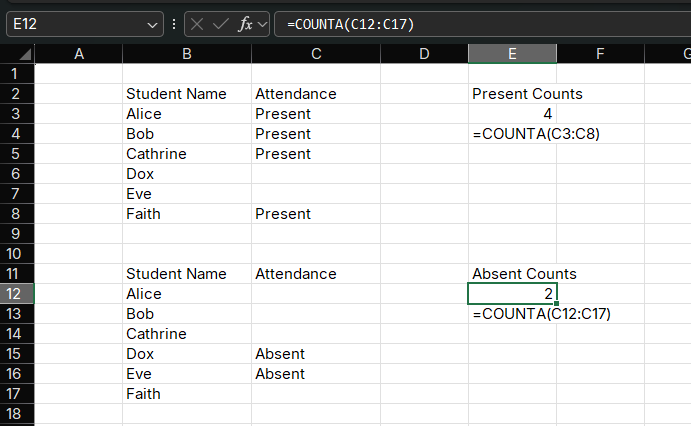
Example: Tracking Student Attendance
Suppose you have student names in column A and attendance records in column B ("Present" or "Absent").
Formula:
=COUNTA(B2:B50)How it works:
- Counts all non-empty cells in the range
- Includes cells with text, numbers, and logical values
- Ignores only completely blank cells
Key Difference: COUNT vs COUNTA
- COUNT: Counts only numeric values
- COUNTA: Counts all non-empty cells (text, numbers, logical values)
COUNTBLANK Function
COUNTBLANK counts the number of empty cells in a range.
Syntax
=COUNTBLANK(range)Argument Explained:
- range: The cell range to check for blank cells (required)
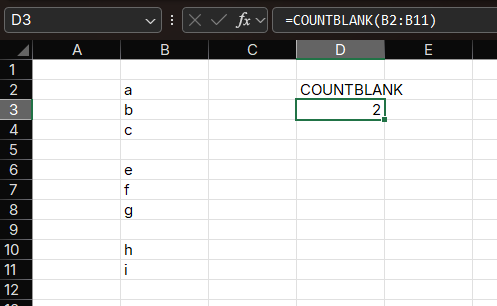
Example: Inventory Management
Suppose you have a list of products in column A and their stock levels in column B. You want to count how many products have no stock recorded.
Formula:
=COUNTBLANK(B2:B100)How it works:
- Counts only completely blank cells in the range
- Ignores cells with formulas that return empty strings (use
=COUNTIF(range, "=")for that)
COUNTIF Function
COUNTIF counts cells that meet a single condition.
Syntax
=COUNTIF(range, criteria)Arguments Explained:
- range: The cell range to evaluate (required)
- criteria: The condition to apply (required, can be a number, text, or expression)
Example 1: Counting Sales Above a Threshold
Suppose you have sales data in column C and want to count how many sales are above $1,000.
Formula:
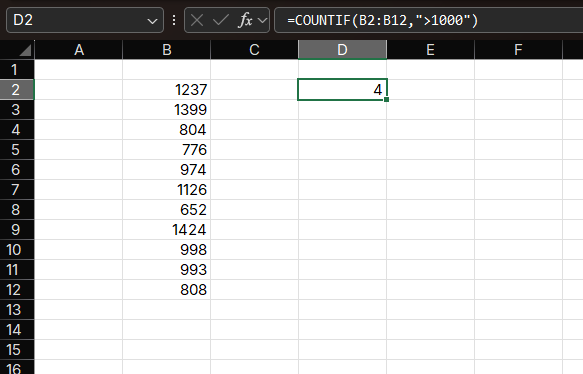
=COUNTIF(C2:C100, ">1000")How it works:
- Evaluates each cell in C2:C100
- Counts cells where the value is greater than 1000
Example 2: Counting Text Values
You can also count cells containing specific text:
Formula:
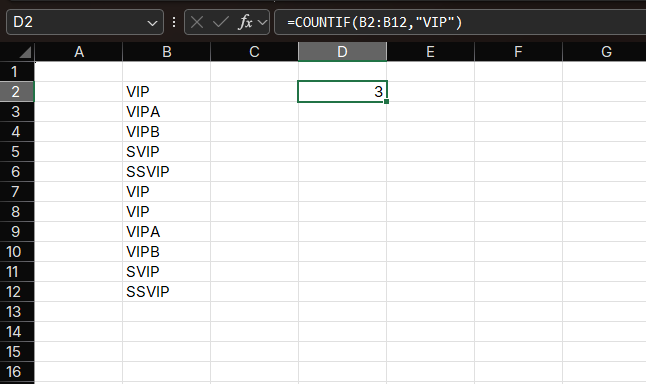
=COUNTIF(D2:D100, "VIP")How it works:
- Counts cells that exactly match "VIP"
- Use wildcards for partial matches:
VIPfor any cell containing "VIP"
Example 3: Using Cell References as Criteria
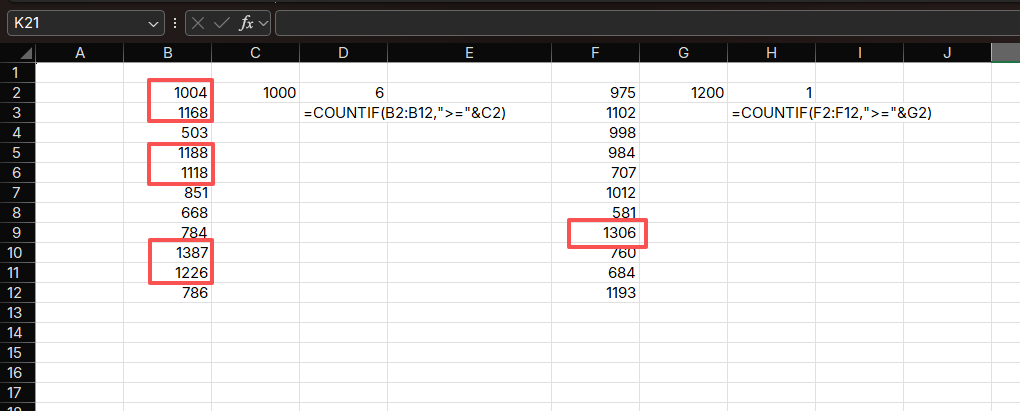
=COUNTIF(E2:E100, ">="&F2)How it works:
- Compares each cell in E2:E100 to the value in F2
- Counts cells that are greater than or equal to F2
COUNTIFS Function
COUNTIFS counts cells that meet multiple conditions.
Syntax
=COUNTIFS(criteria_range1, criteria1, [criteria_range2, criteria2], ...)Arguments Explained:
- criteria_range1: The first range to evaluate (required)
- criteria1: The condition for the first range (required)
- criteria_range2, criteria2, ...: Additional ranges and conditions (optional)
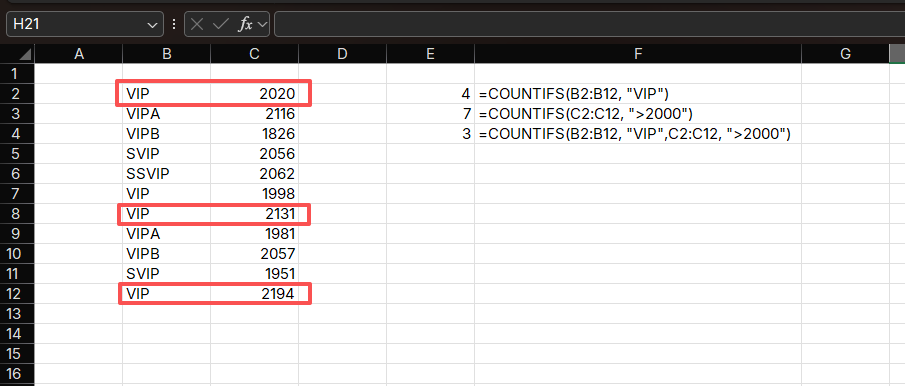
Example 1: Counting High-Value VIP Sales
Suppose you have sales data with customer types in column D and sales amounts in column C. You want to count VIP sales above $2,000.
Formula:
=COUNTIFS(D2:D100, "VIP", C2:C100, ">2000")How it works:
- Checks two conditions:
- Customer type is "VIP"
- Sales amount > $2,000
- Counts only cells that meet both conditions
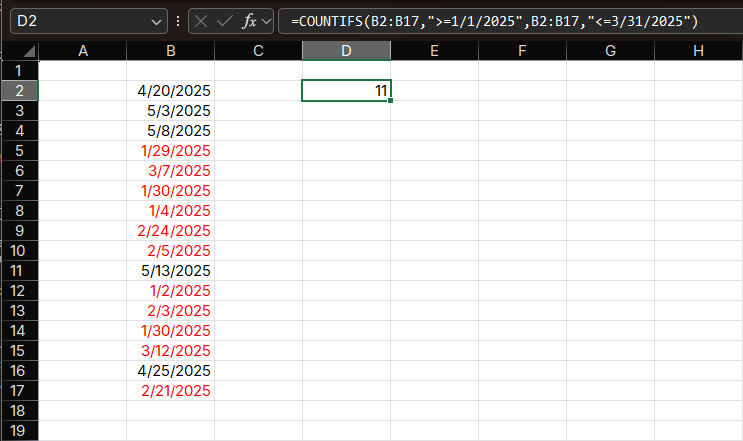
Example 2: Date Range Counting
Count sales between two dates:
Formula:
=COUNTIFS(A2:A100, ">=1/1/2025", A2:A100, "<=3/31/2025")How it works:
- Counts sales transactions in Q1 2025
- Both date conditions must be met
Example 3: Multiple Text Criteria
Count products that are both "Electronics" and "In Stock":
Formula:
=COUNTIFS(B2:B100, "Electronics", E2:E100, "In Stock")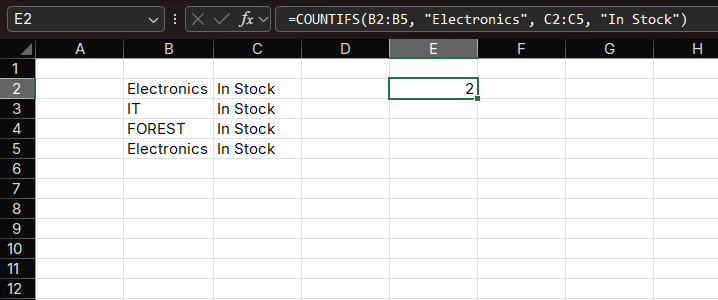
Practical Applications
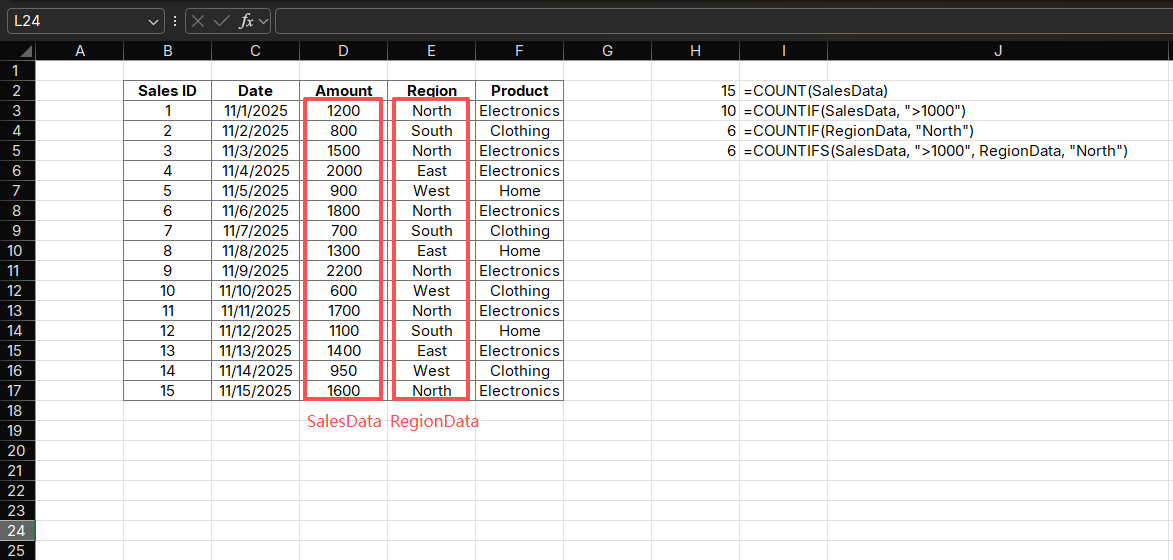
Application 1: Sales Performance Dashboard
Create a comprehensive sales dashboard using multiple COUNT functions:
Formulas:
=COUNT(SalesData) // Total transactions
=COUNTIF(SalesData, ">1000") // High-value sales
=COUNTIF(RegionData, "North") // North region sales
=COUNTIFS(SalesData, ">1000", RegionData, "North") // High-value North salesPurpose: Build a dashboard to track sales performance across regions
How it works:
- Combines multiple COUNT functions to create a comprehensive view
- Provides quick insights into sales distribution and performance
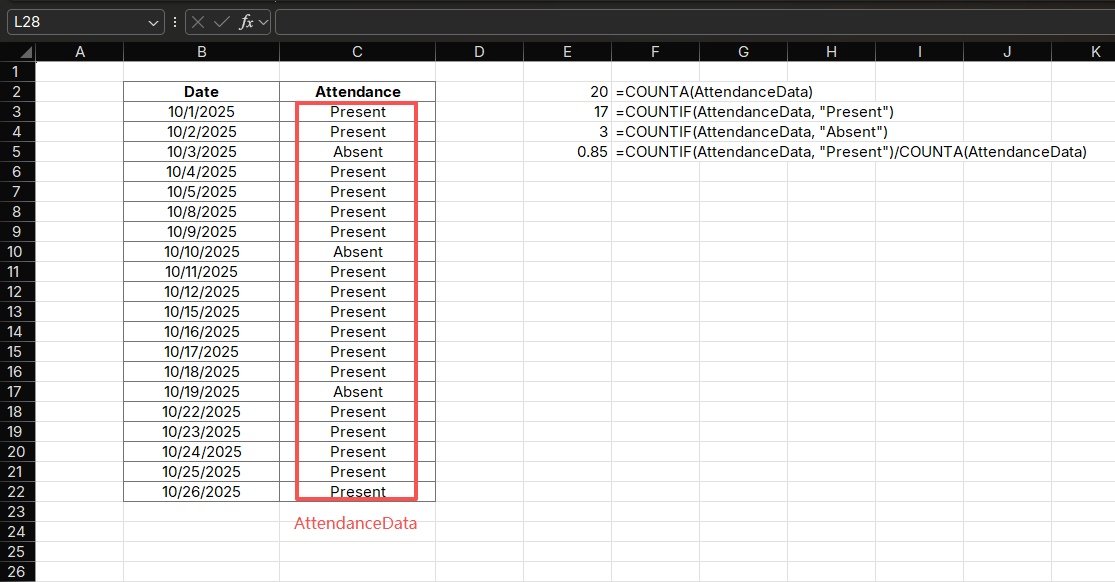
Application 2: Student Attendance Analysis
Analyze attendance patterns using a combination of COUNT functions:
Formulas:
=COUNTA(AttendanceData) // Total classes
=COUNTIF(AttendanceData, "Present") // Present days
=COUNTIF(AttendanceData, "Absent") // Absent days
=COUNTIF(AttendanceData, "Present")/COUNTA(AttendanceData) // Attendance ratePurpose: Calculate attendance statistics for a student
How it works:
- Uses COUNTA to count total classes
- Uses COUNTIF to count present and absent days
- Calculates attendance rate by combining results
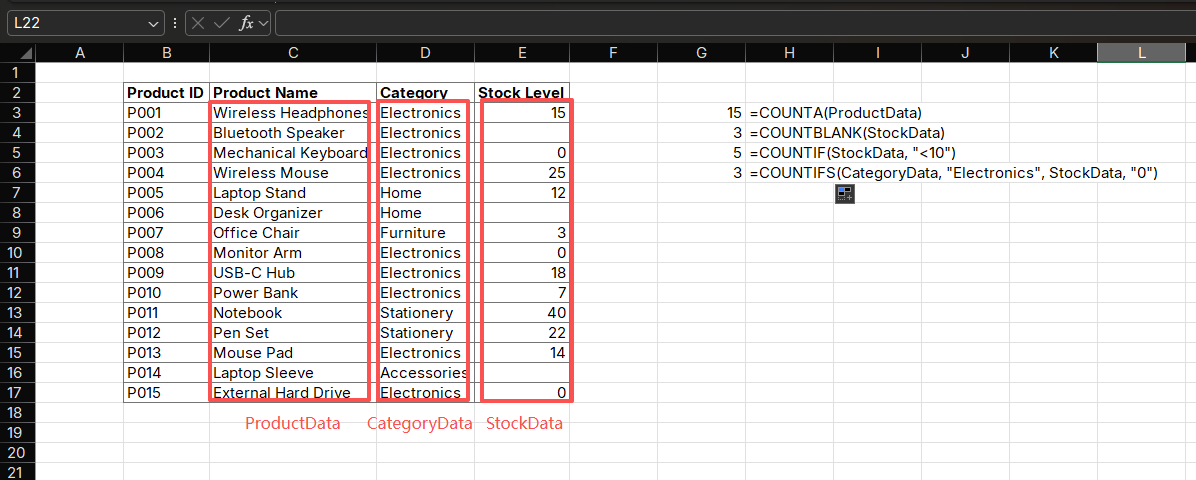
Application 3: Inventory Audit Report
Generate an inventory audit report:
Formulas:
=COUNTA(ProductData) // Total products
=COUNTBLANK(StockData) // Products with no stock
=COUNTIF(StockData, "<10") // Low stock products (<10 units)
=COUNTIFS(CategoryData, "Electronics", StockData, "0") // Out-of-stock electronicsPurpose: Identify inventory issues and prioritize restocking
How it works:
- Uses COUNTA to count total products
- Uses COUNTBLANK to identify missing stock data
- Uses COUNTIF and COUNTIFS to identify low and out-of-stock items
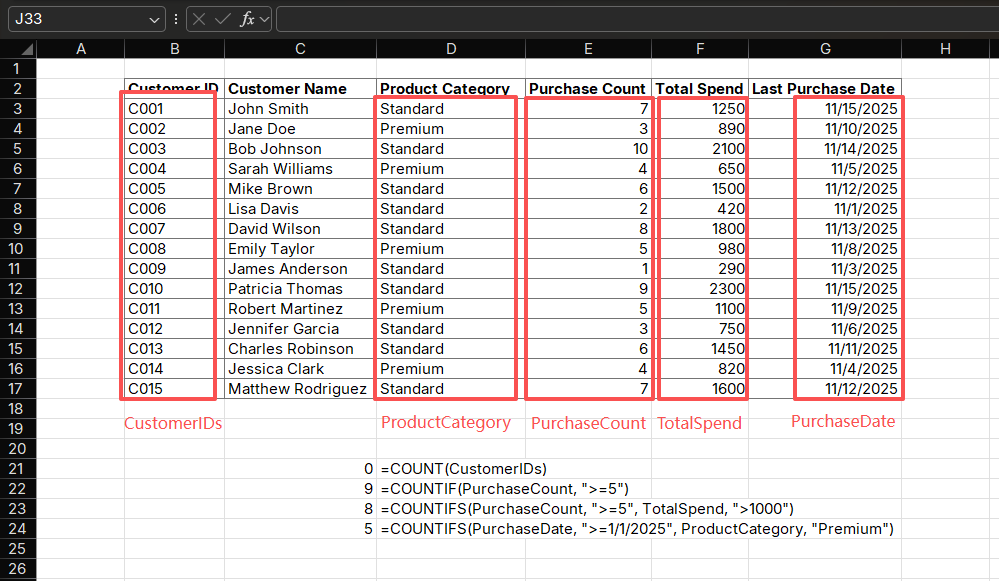
Application 4: Customer Purchase Behavior Analysis
Analyze customer purchase patterns:
Formulas:
=COUNT(CustomerIDs) // Total customers
=COUNTIF(PurchaseCount, ">=5") // Frequent buyers (5+ purchases)
=COUNTIFS(PurchaseCount, ">=5", TotalSpend, ">1000") // High-value frequent buyers
=COUNTIFS(PurchaseDate, ">=1/1/2025", ProductCategory, "Premium") // Premium purchases this yearPurpose: Segment customers based on purchase behavior
How it works:
- Uses COUNT to count total customers
- Uses COUNTIF to identify frequent buyers
- Uses COUNTIFS to create more targeted customer segments
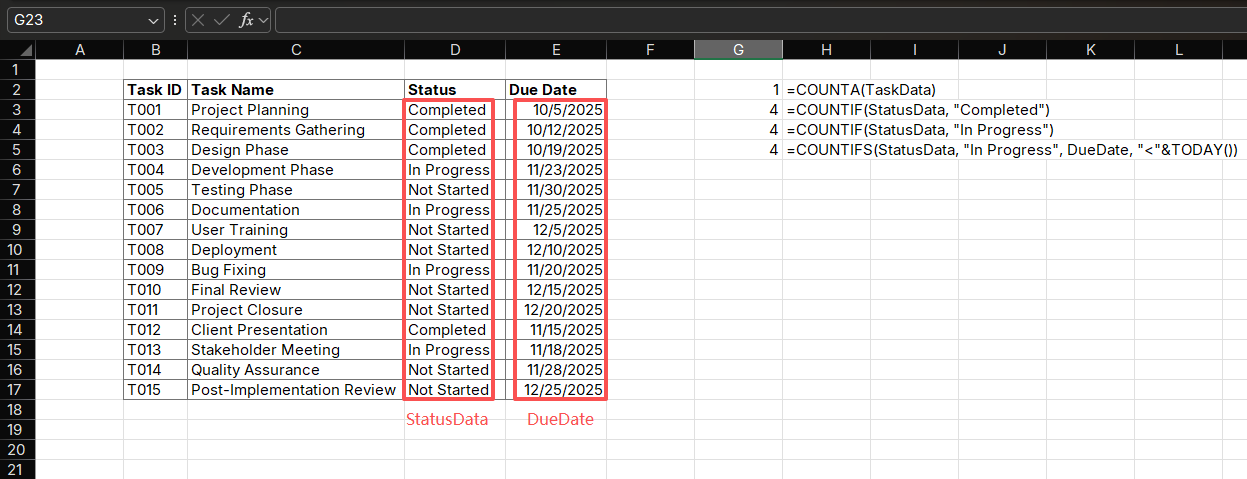
Application 5: Project Task Status Tracking
Track project tasks using COUNT functions:
Formulas:
=COUNTA(TaskData) // Total tasks
=COUNTIF(StatusData, "Completed") // Completed tasks
=COUNTIF(StatusData, "In Progress") // Tasks in progress
=COUNTIFS(StatusData, "In Progress", DueDate, "<"&TODAY()) // Overdue tasksPurpose: Monitor project progress and identify overdue tasks
How it works:
- Uses COUNTA to count total tasks
- Uses COUNTIF to track task statuses
- Uses COUNTIFS with TODAY() function to identify overdue tasks
Common Errors and Troubleshooting
1. COUNT Returns 0 When Expecting a Value
Issue: Cells contain numbers formatted as text.
Fix: Convert text to numbers: Select cells > Data > Text to Columns > Finish
2. COUNTIF Not Working with Text
Issue: Missing quotation marks around text criteria.
Fix: Add quotes: =COUNTIF(A2:A10, "Text") instead of =COUNTIF(A2:A10, Text)
3. COUNTIFS Returns Incorrect Results
Issue: Mismatched ranges (different sizes).
Fix: Ensure all criteria ranges have the same number of rows and columns.
4. COUNTBLANK Doesn't Count Formula Blanks
Issue: Cells contain formulas that return empty strings.
Fix: Use =COUNTIF(range, "=") to count formula blanks.
5. Wildcard Issues
Issue: Partial matches not working . Fix: Use correct wildcards:
*for any number of characters?for a single character~to escape wildcards (e.g.,~*to find actual asterisks)
Summary
The COUNT function family provides powerful tools for data analysis:
- COUNT: Counts numeric values
- COUNTA: Counts non-empty cells
- COUNTBLANK: Counts empty cells
- COUNTIF: Counts with single conditions
- COUNTIFS: Counts with multiple conditions
By mastering these functions, you can:
- Analyze sales performance
- Track attendance and participation
- Manage inventory levels
- Segment customers
- Generate valuable business insights
Start using these functions today to unlock the full potential of your Excel data analysis!
Have a problem with Excel or Google Sheets?
Tell us about the issue you're facing, and we'll create a step-by-step guide for it.